Data cleaning with Tidyverse
Reka Toth
2022-05-18
Source:vignettes/data_cleaning.Rmd
data_cleaning.RmdClean data:
- one information, one variable
- one row per observation
- data and type matches
- same name for same categories
- clean factors, if necessary
library(tidyverse)
#> ── Attaching packages ─────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.1 ──
#> ✔ ggplot2 3.3.6 ✔ purrr 0.3.4
#> ✔ tibble 3.1.7 ✔ dplyr 1.0.9
#> ✔ tidyr 1.2.0 ✔ stringr 1.4.0
#> ✔ readr 2.1.2 ✔ forcats 0.5.1
#> ── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
library(nycflights13)
library(magrittr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'magrittr'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:purrr':
#>
#> set_names
#> The following object is masked from 'package:tidyr':
#>
#> extractExercise
- Clean up the following dataset: messy_data.xlsx messy_data.txt
Tidyverse
Dplyr
select() extracts columns and returns a tibble.
arrange() changes the ordering of the rows.
filter() picks cases based on their values.
mutate() adds new variables that are functions of existing variables.
rename() easily changes the name of a column(s)
summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary.
group_by() groups observations
pull() extracts a single column as a vector.
_join() group of functions that merge two data frames together, includes (inner_join(), left_join(), right_join(), and full_join()).
Examples
data("flights")
flights %>%
select(year, month, day) %>%
head()
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> year month day
#> <int> <int> <int>
#> 1 2013 1 1
#> 2 2013 1 1
#> 3 2013 1 1
#> 4 2013 1 1
#> 5 2013 1 1
#> 6 2013 1 1
flights %>%
select(year:dep_time, ends_with("time")) %>%
head()
#> # A tibble: 6 × 8
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time arr_time sched_arr_time air_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 515 830 819 227
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 529 850 830 227
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 540 923 850 160
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 545 1004 1022 183
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 600 812 837 116
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 558 740 728 150
flights %>%
select(year:dep_time, ends_with("time")) %>%
arrange(desc(air_time)) %>%
head()
#> # A tibble: 6 × 8
#> year month day dep_time sched_dep_time arr_time sched_arr_time air_time
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 2013 3 17 1337 1335 1937 1836 695
#> 2 2013 2 6 853 900 1542 1540 691
#> 3 2013 3 15 1001 1000 1551 1530 686
#> 4 2013 3 17 1006 1000 1607 1530 686
#> 5 2013 3 16 1001 1000 1544 1530 683
#> 6 2013 2 5 900 900 1555 1540 679
flights_sml <- flights %>%
head(n=100)
flights_sml %>%
filter(month==3 & year==2013)
#> # A tibble: 0 × 19
#> # … with 19 variables: year <int>, month <int>, day <int>, dep_time <int>,
#> # sched_dep_time <int>, dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
#> # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
#> # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
#> # hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>
flights_sml %>%
select(year:dep_time) %>%
mutate(date=paste(year, month, day))
#> # A tibble: 100 × 5
#> year month day dep_time date
#> <int> <int> <int> <int> <chr>
#> 1 2013 1 1 517 2013 1 1
#> 2 2013 1 1 533 2013 1 1
#> 3 2013 1 1 542 2013 1 1
#> 4 2013 1 1 544 2013 1 1
#> 5 2013 1 1 554 2013 1 1
#> 6 2013 1 1 554 2013 1 1
#> 7 2013 1 1 555 2013 1 1
#> 8 2013 1 1 557 2013 1 1
#> 9 2013 1 1 557 2013 1 1
#> 10 2013 1 1 558 2013 1 1
#> # … with 90 more rows
try(flights_sml %>%
select(year:dep_time) %>%
mutate(speed=distance/air_time *60))
#> Error in mutate(., speed = distance/air_time * 60) :
#> Problem while computing `speed = distance/air_time * 60`.
#> Caused by error:
#> ! object 'distance' not found
flights_sml %>%
select(distance, air_time) %>%
mutate(speed=distance/air_time *60)
#> # A tibble: 100 × 3
#> distance air_time speed
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1400 227 370.
#> 2 1416 227 374.
#> 3 1089 160 408.
#> 4 1576 183 517.
#> 5 762 116 394.
#> 6 719 150 288.
#> 7 1065 158 404.
#> 8 229 53 259.
#> 9 944 140 405.
#> 10 733 138 319.
#> # … with 90 more rows
flights %>%
select(year:arr_delay) %>%
group_by(month) %>%
summarise(mean_delay=mean(arr_delay, na.rm=T), sd=sd(arr_delay, na.rm=T))
#> # A tibble: 12 × 3
#> month mean_delay sd
#> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 6.13 40.4
#> 2 2 5.61 39.5
#> 3 3 5.81 44.1
#> 4 4 11.2 47.5
#> 5 5 3.52 44.2
#> 6 6 16.5 56.1
#> 7 7 16.7 57.1
#> 8 8 6.04 42.6
#> 9 9 -4.02 39.7
#> 10 10 -0.167 32.6
#> 11 11 0.461 31.4
#> 12 12 14.9 46.1
flights %>%
select(year:dest) %>%
group_by(month, dest) %>%
summarise(mean_delay=mean(arr_delay, na.rm=T), sd=sd(arr_delay, na.rm=T), count=n())
#> `summarise()` has grouped output by 'month'. You can override using the
#> `.groups` argument.
#> # A tibble: 1,113 × 5
#> # Groups: month [12]
#> month dest mean_delay sd count
#> <int> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 1 ALB 35.2 68.1 64
#> 2 1 ATL 4.15 34.2 1396
#> 3 1 AUS 8.72 48.6 169
#> 4 1 AVL 23.5 55.9 2
#> 5 1 BDL 11.0 51.2 37
#> 6 1 BHM 16.7 70.0 25
#> 7 1 BNA 12.7 47.0 399
#> 8 1 BOS -2.54 28.6 1245
#> 9 1 BQN 2.65 30.0 93
#> 10 1 BTV 6.67 36.5 223
#> # … with 1,103 more rowspivot_wider, pivot_longer
Examples from here:
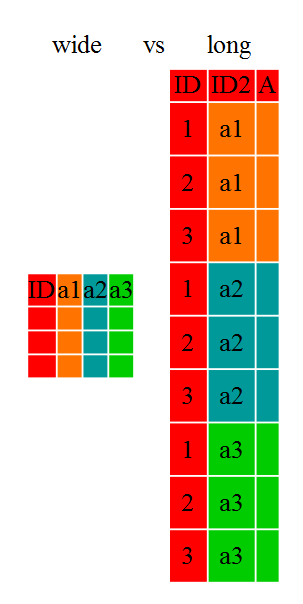
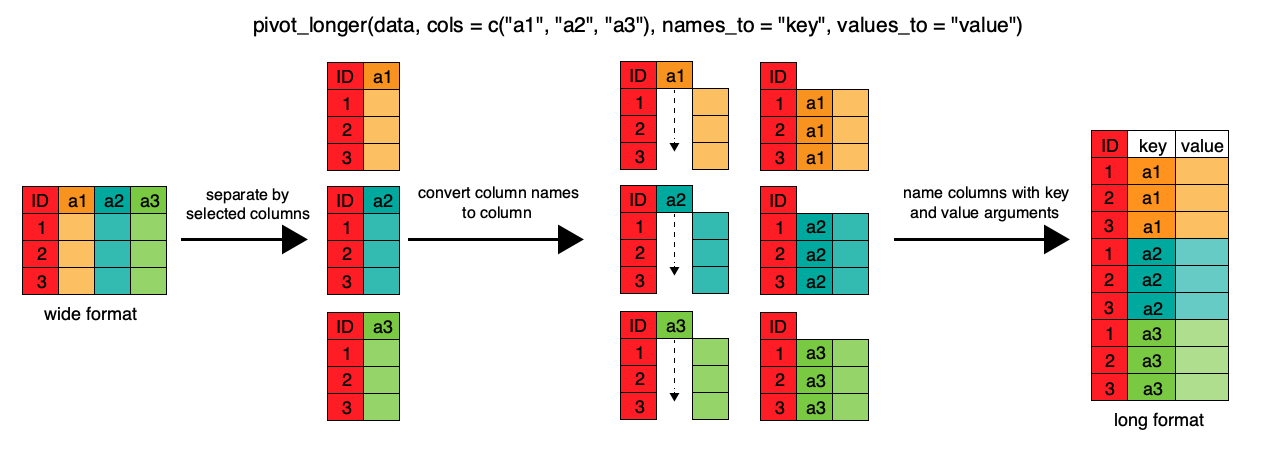
library(gapminder)
gap_wide <- gapminder %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = year, values_from = c(pop, gdpPercap,lifeExp ))
gap_long <- gap_wide %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = c(-continent, -country),
names_to = "obstype_year", values_to = "obs_values"
) %>%
separate(obstype_year, into = c('obs_type', 'year'), sep = "_")
Exercises
Let’s add a variable to ‘flights’ Air time in hours
Which carrier has the worst arrival delays
Which carrier has the most flights?
arrange: The more flights per carrier, the higher/lower the arrival delay”
Merging
merge and join_
data("mtcars")
mtcars1 <- mtcars[1:30,1:4]
mtcars2 <- mtcars[3:32,5:8]
mtcars1 <- rownames_to_column(mtcars1, var="model")
mtcars1 <- mtcars1[c(1:30, 1),]- Clean the messy data with tidyverse